Table of Contents
Identity and Access Management
Azure AD
- Custom AAD roles require a P1 or P2 license
- Because Azure AD is HTTP/HTTPS based, it does not use Kerberos authentication. Instead, it uses HTTP and HTTPS protocols such as SAML, WS-Federation, and OpenID Connect for authentication (and OAuth for authorization).
- MFA is supported for free tier AAD by way of Security Defaults.
- Security Defaults is a built-in set of protections against identity-based attacks.
- delegated administration is the term for how a CSP (Cloud Solution Provider) can be given roles that allow them to administer services on behalf of the customer.
Security Principle
Security principal: An Azure security principal is a security identity that user-created apps, services, and automation tools use to access specific Azure resources. Think of it as a “user identity” (username and password or certificate) with a specific role, and tightly controlled permissions. A security principal should only need to do specific things, unlike a general user identity. It improves security if you grant it only the minimum permission level that it needs to perform its management tasks. A security principal used with an application or service is called a service principal.
Authentication Methods
Azure AD Pass-through Authentication (PTA)
Using PTA AAD passes authentication attempts to an agent running on an on-prem server that passes it to an on-prem Windows Server AD.
Provides a simple password validation for Azure AD authentication services by using a software agent that runs on one or more on-premises servers. The servers validate the users directly with your on-premises Active Directory, which ensures that the password validation doesn't happen in the cloud. Companies with a security requirement to immediately enforce on-premises user account states, password policies, and sign-in hours might use this authentication method.
Azure AD password hash synchronization
Password hash sync works by running the Azure AD Connect service on a server on-prem that syncs user and password hashes to AAD.
The simplest way to enable authentication for on-premises directory objects in Azure AD. Users can use the same username and password that they use on-premises without having to deploy any additional infrastructure. Some premium features of Azure AD, like Identity Protection and Azure AD Domain Services, require password hash synchronization, no matter which authentication method you choose.
AAD Roles
- AAD Roles are generally assigned to individual users, but some groups are given a special designation that allows roles to be assigned to them.
- These must be cloud groups created directly in AAD, not synced security groups from Windows AD.
- The members must be directly assigned to the group—not dynamic groups.
- AAD does not have organizational units (OUs)—it has a flat structure. But it does have Administrative Units that certain roles can be assigned to.
The Account Administrator is the user that initially signed up for the Azure subscription, and is responsible as the billing owner of the subscription.
Only the Billing Administrator of an account can transfer ownership of a subscription.
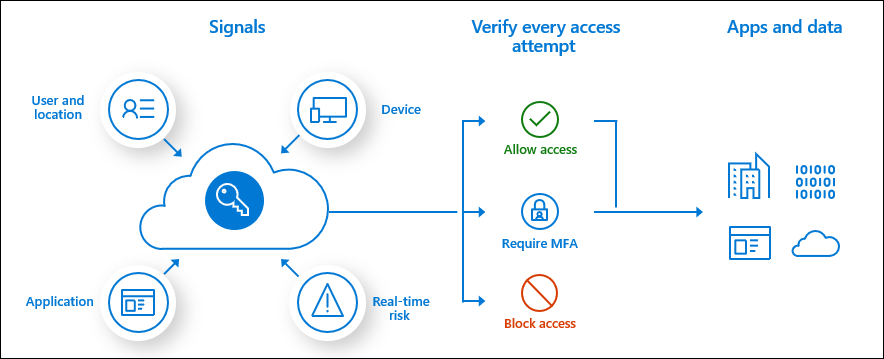
Conditional Access
- Conditional Access is a capability that takes in various signals and determines whether a given user should be granted access to resources.
- Conditional Access is recommended over per-user MFA requirements for requiring MFA.
- Conditional Access requires a AAD P1 license, but the risk-based policy capabilties requires a P2 license
- When a user/group is both included and excluded in a policy the exclusion overrides the inclusion.
- If there are more than one policies with criteria that is met and one grants access and another blocks access the block policy will take effect over the grant policy.
Examples of conditions
- Require multi-factor authentication.
- Require device to be marked as compliant.
- Require hybrid Azure AD joined device.
- Require approved client app.
- Require app protection policy.
- Require password change.
Control user access based on session controls to enable limited experiences within specific cloud applications. As an example, Conditional Access App Control uses signals from Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to block the download, cut, copy, and print capabilities for sensitive documents, or to require labeling of sensitive files. Other session controls include sign-in frequency and application enforced restrictions that, for selected applications, use the device information to provide users with a limited or full experience, depending on the device state.
App Identity
When you have applications, hosted services, or automated tools that needs to access or modify resources, you can create an identity for the app. This identity is known as a service principal.
For services that support Managed Identities they should be used instead of service principles.
Managed Identities
- Managed Identities provides Azure services with automatically managed identity in AAD. You can use the identity with any service that supports AAD, like Azure Key Vault.
Types
- System-assigned. Some Azure services allow you to enable a managed identity directly on a service instance. When you enable a system-assigned managed identity, an identity is created in Azure AD. The identity is tied to the lifecycle of that service instance. When the resource is deleted, Azure automatically deletes the identity for you. By design, only that Azure resource can use this identity to request tokens from Azure AD
- User-assigned. You may also create a managed identity as a standalone Azure resource. You can create a user-assigned managed identity and assign it to one or more instances of an Azure service. For user-assigned managed identities, the identity is managed separately from the resources that use it.
Examples of System-assigned
- A VM accessing an Azure Key Vault
- A VM accessing Azure Storage
- A Azure App Service accessing an Azure Key Vault
Terminology
- Client ID
- Principle ID
- Azure Instance Metadata Service (IMDS)
Administrative Units
- An Administrative Unit (AU) is a mechanism for limiting the permissions of an Azure AD role to apply to a selected set of users and/or groups instead of an entire AAD directory. It limits the scope of the role. When a group is selected the scope only applies to the group itself, not the users that are a member of the group.
An administrative unit is an Azure AD resource that can be a container for other Azure AD resources. An administrative unit can contain only users, groups, or devices.
- An administrative unit is similar in some ways to an organization unit in traditional AD.
- A AAD P1 license or better is required for each AU administrator, but members can be AAD free license or better.
- To create an Administrative Unit the user must be a Global Administrator or Privileged Role Administrator.
Applications and Permissions
- Delegated permissions are used by apps that have a signed-in user present.
- Application permissions are used by apps that run without a signed-in user present, for example, apps that run as background services or daemons.
Access Reviews
- Requires a P2 license
Microsoft Entra Verified ID
Passwordless authentication
User Management
- Deleted users and M365 groups can be restored (undeleted) for up to 30 days.
- Deleted Security Groups cannot be restored.
Guest Access
- The default user/guest collaboration settings allow any user (including B2B guest uers) to invite guest users.
- When inviting guests is limited to certain admin roles those roles include Global Administrator, User Administrator, and Guest Inviter.