Table of Contents
Data and Application Security
Meta
- Need to spend a lot of time on understanding these topics.
Configure security for storage
- Configure access control for storage accounts
- Configure storage account access keys
- Configure Azure AD authentication for Azure Storage and Azure Files
- Configure delegated access
- Data sovereignty is the concept that information, which has been converted and stored in binary digital form, is subject to the laws of the country or region in which it is located.
Configure security for data
- Enable database authentication by using Azure AD
- Enable database auditing
- Configure dynamic masking on SQL workloads
- Implement database encryption for Azure SQL Database
- Implement network isolation for data solutions, including Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Cosmos DB
Configure and manage Azure Key Vault
- Create and configure Key Vault
- Configure access to Key Vault
- Manage certificates, secrets, and keys
- Configure key rotation
- Configure backup and recovery of certificates, secrets, and keys
Azure Key Vault
- Key Vault is used to store and manage tokens, passwords, certificates, encryption keys, API keys, and other secrets.
- Authentication and authorization for Key Vault is handled by Azure AD.
- There are two levels of the service, standard and premium.
- Only premium can use hardware (HSM) for key encryption. This is the only difference between standard and premium Key Vault.
- A third option is a Managed HSM that only supports HSM backed keys. It does not support any other type of secrets.
- Soft keys: A key processed in software by Key Vault, but is encrypted at rest using a system key that is in an Hardware Security Module (HSM). Clients may import an existing RSA or EC (Elliptic Curve) key, or request that Key Vault generate one.
- Hard keys: A key processed in an HSM (Hardware Security Module). These keys are protected in one of the Key Vault HSM Security Worlds (there's one Security World per geography to maintain isolation). Clients may import an RSA or EC key, in soft form or by exporting from a compatible HSM device. Clients may also request Key Vault to generate a key.
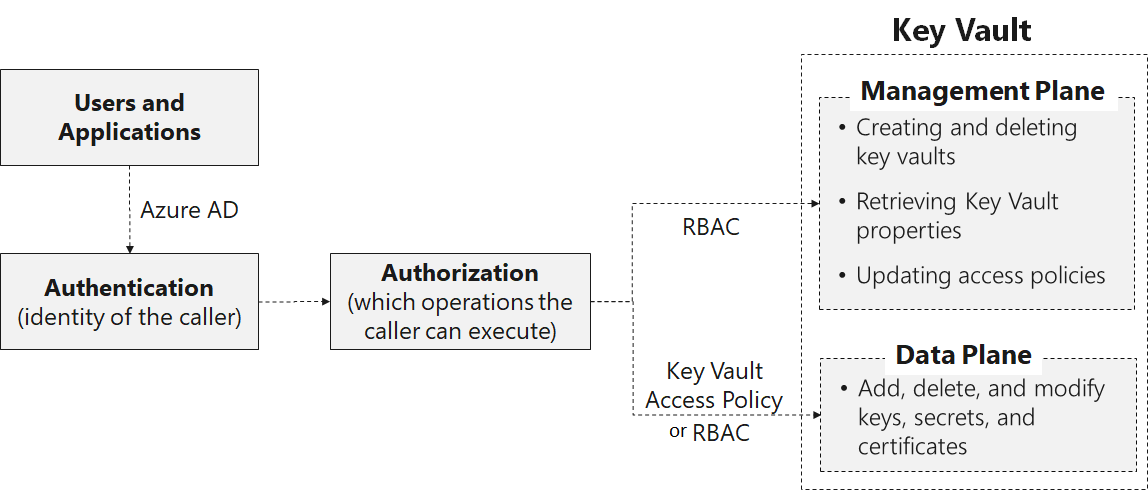
- There are two methods for managing access to key vaults and their contents. One is vault access policies and the other is RBAC role policies.
- The control plane is where the key vault and access is created/modified/ deleted and the data plane is where the contents of the key vault are accessed.
To access a key vault in either plane, all callers (users or applications) must have proper authentication and authorization. Authentication establishes the identity of the caller. Authorization determines which operations the caller can execute.
Both planes use Azure AD for authentication. For authorization, the management plane uses RBAC, and the data plane can use either newly added RBAC or a Key Vault access policy.
If a user has contributor permissions (RBAC) to a key vault management plane, they can grant themselves access to the data plane by setting a key vault access policy. We recommend that you tightly control who has contributor access to your key vaults, to ensure that only authorized persons can access and manage your key vaults, keys, secrets, and certificates.
Supported Operations
- Sign and Verify: Strictly, this operation is “sign hash” or “verify hash”, as Key Vault doesn't support hashing of content as part of signature creation. Applications should hash the data to be signed locally, then request that Key Vault sign the hash. Verification of signed hashes is supported as a convenience operation for applications that may not have access to [public] key material.
- Key Encryption / Wrapping: A key stored in Key Vault may be used to protect another key, typically a symmetric content encryption key (CEK). When the key in Key Vault is asymmetric, key encryption is used. When the key in Key Vault is symmetric, key wrapping is used.
- Encrypt and Decrypt: A key stored in Key Vault may be used to encrypt or decrypt a single block of data. The size of the block is determined by the key type and selected encryption algorithm. The Encrypt operation is provided for convenience, for applications that may not have access to [public] key material.
HSM
- Hardware Security Module is a hardware based solution for storing keys.
Microsoft Identity Platform
The Microsoft identity platform performs identity and access management (IAM) only for registered applications. Whether it's a client application like a web or mobile app, or it's a web API that backs a client app, registering it establishes a trust relationship between your application and the identity provider, the Microsoft identity platform.
Managed Identities
- Managed Identities provides Azure services with automatically managed identity in AAD. You can use the identity with any service that supports AAD, like Azure Key Vault.
Types
- System-assigned. Some Azure services allow you to enable a managed identity directly on a service instance. When you enable a system-assigned managed identity, an identity is created in Azure AD. The identity is tied to the lifecycle of that service instance. When the resource is deleted, Azure automatically deletes the identity for you. By design, only that Azure resource can use this identity to request tokens from Azure AD.
- User-assigned. You may also create a managed identity as a standalone Azure resource. You can create a user-assigned managed identity and assign it to one or more instances of an Azure service. For user-assigned managed identities, the identity is managed separately from the resources that use it.
Terminology
- Client ID
- Principle ID
- Azure Instance Metadata Service (IMDS)
Database Security
SQL Database Authentication
- AAD is recommended over native SQL Server authentication for database authentication
SQL Authentication
With this authentication method, the user submits a user account name and associated password to establish a connection. This password is stored in the master database for user accounts linked to a login or stored in the database containing the user accounts not linked to a login.
Logins and users: In Azure SQL, a user account in a database can be associated with a login that is stored in the master database or can be a user name that is stored in an individual database
- A login is an individual account in the master database, to which a user account in one or more databases can be linked. With a login, the credential information for the user account is stored with the login.
- A user account is an individual account in any database that may be but does not have to be linked to a login. With a user account that is not linked to a login, the credential information is stored with the user account.
- Recommendation: Use Azure Active Directory authentication to centrally manage identities of database users and as an alternative to SQL Server authentication.
AAD Authentication
SQL Database Firewalls
- Initially, all access to your Azure SQL Database is blocked by the SQL Database firewall.
- To help protect your data, firewalls prevent all access to your database server until you specify which computers have permission. The firewall grants access to databases based on the originating IP address of each request.
- There are server-level IP firewall rules and database-level IP firewall rules. Server-level apply to all databases on the server and since the scope is broader they are evaluated after database-level rules.
- Recommendation: Whenever possible, as a best practice, use database-level IP firewall rules to enhance security and to make your database more portable. Use server-level IP firewall rules for administrators and when you have several databases with the same access requirements, and you don't want to spend time configuring each database individually.
Auditing
Auditing for Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics tracks database events and writes them to an audit log in your Azure storage account, Log Analytics workspace or Event Hubs.
- Auditing can be enabled at the server-level or database-level
Data Discovery and Classification
- Data Discovery and Classification is the process of detecting and labeling sensitive data.
§
- TDE (Transparent data encryption) performs real-time I/O encryption and decryption of the data at the page level.
§
HDInsight
- To support multiuser access an HDInsight cluster requires AADDS.