This is an old revision of the document!
Identity and Access Management
Users and Groups
- Security groups: Used to manage user and computer access to shared resources.
- Microsoft 365 groups: Provides collaboration opportunities by giving group members access to a shared mailbox, calendar, files, SharePoint sites, and more.
- M365 can be setup to expire after a specified period of time
- When a group expires, almost all of its associated services (the mailbox, Planner, SharePoint site, team, etc.) are also deleted.
- When a group expires it is “soft-deleted” which means it can still be recovered for up to 30 days.
- Expiration policies are only supported for dynamic groups.
- Entra ID Security groups do not support expiration policies.
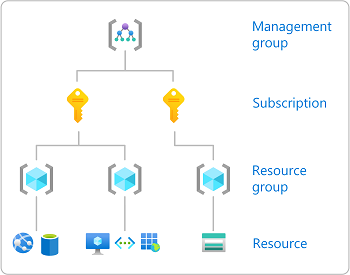
Azure Organization/Structure/Scoping
- Within the Azure ecosystem there are several organizational structures
Management Groups
- Management groups provide a governance scope (for Azure Resources) above subscriptions.
- By moving multiple subscriptions under a management group, you can create one Azure role assignment on the management group. The role will inherit that access to all the subscriptions.
- A management group tree can support up to six levels of depth.
Administrative Units
- Administrative Units (AU) provide an administrative scope over a subset Entra ID users and groups.
- Adding a group to an administrative unit brings the group itself into the management scope of the administrative unit, but not the members of the group.
- AUs cannot be nested.
Control Plane vs. Data Plane
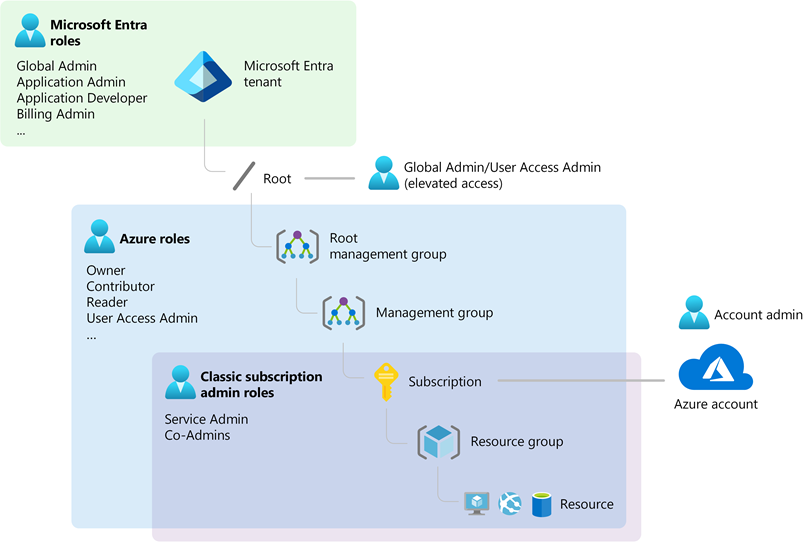
Microsoft Entra ID vs. Azure Roles
- ARM (Azure Resource Manager)/Azure/RBAC roles are distinct from Azure Entra ID roles.
- And Data Access roles/permissions are distinct from resource access roles/permissions. For example, having the Owner role for a storage account does not give a user access to the data in the storage account.
- The control plane permissions are distinct from the data plane permissions.
- Entra ID roles (sometimes referred to as Administrative Roles) are used for managing access to identity objects within the Entra ID tenant itself.
- Although Microsoft Entra ID roles are typically set at a tenant level, you can make scope adjustments using administrative units.
- Azure RBAC roles are used for managing access to resources in an Azure subscription
- Examples of Azure roles:
- Owner - this is role with the highest level of access, which includes the ability to grant users access to resources
- Contributor - this role grants permissions for read/write access to the scope it's assigned to, but (unlike Owner) it does not grant the permissions needed to assign permissions to principles to access resources.
- Reader
- A role assignment is a combination of an identity, role (permissions), and scope.. This could be thought of as the who, what and where respectively (Is there a better way to say this?).
- With a role there are control plane actions (just referred to as actions) and Data Actions, which are actions at the data plane layer. [Say more about this.]
- The Activity Log shows only control plane logs.
- Microsoft Entra Domain Services provides traditional AD functionality (as-a-service) in Azure. But there are no domain controllers to manage and maintain.
- Supports LDAP, NTLM and Kerberos protocols
Entra ID/Administrative Roles
- Privileged Roles and permissions can be used to delegate management of directory resources to other users, modify credentials, authentication or authorization policies, or access restricted data.
- Examples of Entra ID roles:
- Global Admin
- Application Admin
- Application Developer
- Billing Admin
Azure Roles
- Owner vs. Contributor
- Owner grants full access to manage all resources, including the ability to assign roles in Azure RBAC.
- Contributor grants full access to manage all resources, but does not allow you to assign roles in Azure RBAC, manage assignments in Azure Blueprints, or share image galleries.
- Azure Roles are additive, meaning when multiple roles are assigned to a user the user gets the sum of all permissions granted by all roles.
Administrative Units
- The default scope for Entra Id roles is global (the entire tenant)
- Administrative Units (AU) can be used to limit scope of Entra ID roles to a unit that is a subset of the tenant
- AU's do not apply to resources, they only apply to tenant entities
- Entra ID roles are also referred to as Administrative roles, hence the name Administrative Units
- An administrative unit can contain only users, groups, or devices.
- AU's are used to limit the scope of permissions (for Entra ID roles) to only the users, groups or devices that it contains.
- An example usage would be, assigning someone the Password Administrator role at the AU level, so they can reset non-administrative passwords for only the users in the AU.
- Other examples of permissions that can be assigned to AU's.
- Nesting is not supported
- ☝️Putting groups in an AU does not implicitly give the ability to access and change the attributes of the members of the group. The members must be explicitly added to the AU.
Management Groups
- Management Groups can be used to apply budget, RBAC roles and policies at a scope above subscriptions.
Password Handling
- ❓Does Microsoft 365 Business Standard License support password writeback? Answer: It does not support it. See Docs
Custom Domain Name
- To add a custom domain name to an Entra ID tenant you must create either TXT or MX record for the domain name to verify ownership of the domain.
Microsoft Entra Connect
- The Microsoft Entra Connect synchronization services (Microsoft Entra Connect Sync) is a main component of Microsoft Entra Connect. It takes care of all the operations that are related to synchronize identity data between your on-premises environment and Microsoft Entra ID. Microsoft Entra Connect Sync is the successor of DirSync and Azure AD Sync.
- A server in staging mode is not running password sync or password writeback, even if you selected these features during installation.
- When you disable staging mode, the server starts exporting, enables password sync, and enables password writeback.
User Profile Attributes
By default, Global Administrator and other administrator roles do not have permissions to read, define, or assign custom security attributes.