Enterprise Governance
- Use RBAC and Azure Policy to limit access to your Azure solutions, and determine which method is right for your security goals.
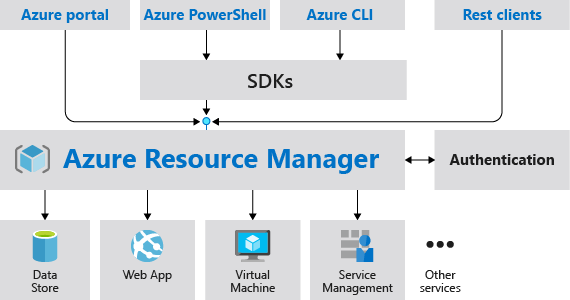
Azure Resource Manager
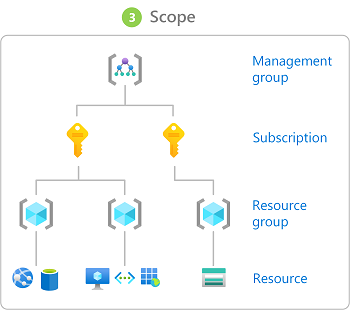
Scope
Management Groups
Management groups provide a governance scope above subscriptions.
- They can be up to six levels deep
- Policies and roles assigned at the Management Group level are inherited by all levels under it.
- This avoids duplicating assignments manually at multiple levels and reduced maintenance.
Use Case Examples
- You can apply policies to a management group that limits the regions available for virtual machine (VM) creation.
- You can give user access to multiple subscriptions using one Azure role assignment.
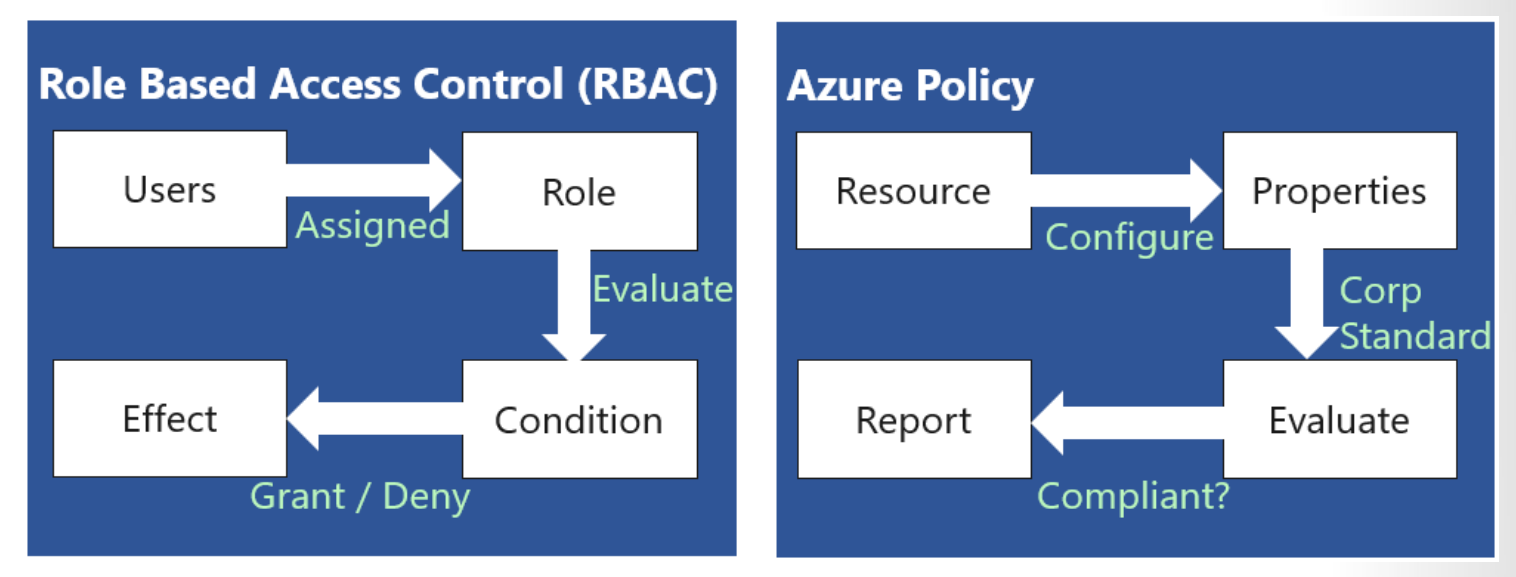
Azure Policy
Azure Policy is a service you use to create, assign, and manage policies. These policies enforce different rules and effects over your resources so that those resources stay compliant with your corporate standards and service level agreements.
- Azure Policy is a free service
- Multiple Azure Policies can be group together to form a policy initiative
- By default policies apply to the scope where they are applied and all child scopes, but scopes can be excluded
- Policies can be applied at all levels of scope supported by Azure (i.e. management group, subscription, resource group, resource). but the policies themselves are defined at either a subscription of management group level.
Three Pillars
- real-time enforcement and compliance assessment
- applying policies at scale
- remediation by leveraging a remediation policy
- Remediation policies will bring resources into compliance; existing resources will be flagged and not remediated to avoid adverse effects to the environment.
Policy Examples
- Ensure only VMs of certain type are created
- Ensure resources are not created in certain regions
- To add tags to resources that need for tracking purposes
Policy Responses
- Deny the resource change
- Log the change to the resource
- Alter the resource before the change
- Alter the resource after the change
- Deploy related compliant resources
RBAC Permissions for Azure Policy
RBAC
RBAC is an authorization system built on Azure Resource Manager that provides fine-grained access management of Azure resources.
- RBAC roles can be assigned at the level of subscription, resource group or resource. Roles at higher levels are inherited by lower levels.
RBAC vs Azure Policies
A few key differences between Azure Policy and RBAC exist. RBAC focuses on user actions at different scopes. You might be added to the contributor role for a resource group, allowing you to make changes to that resource group. Azure Policy focuses on resource properties during deployment and for already-existing resources. Azure Policy controls properties such as the types or locations of resources. Unlike RBAC, Azure Policy is a default-allow-and-explicit-deny system.
Azure Policy focuses on resource properties during deployment and for already-existing resources. Azure Policy controls properties such as the types or locations of resources.
Built-in Roles
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Contributor | Lets you manage everything except granting access to resources. |
| Owner | Lets you manage everything, including access to resources. |
| Reader | Lets you view everything, but not make any changes |
| User Access Administrator | Lets you manage user access to Azure resources. |
Resource Locks
- Resource Locks are an additional layer of protection for resources above what is provided by RBAC roles. It can be used to prevent resources from being changed or deleted.
Azure Blueprints
Blueprints are a declarative way to orchestrate the deployment of various resource templates and other artifacts such as:
- Role Assignments
- Policy Assignments
- Azure Resource Manager templates (ARM templates)
- Resource Groups
Azure Blueprints seem analogous to AWS CloudFormation templates. They are like ARM templates, but the template and it's relationship/association to the resources that are deployed using it are preserved.
- A Blueprint can consist of zero or more ARM templates.
- With Azure Blueprints, the relationship between the blueprint definition (what should be deployed) and the blueprint assignment (what was deployed) is preserved. This connection supports improved tracking and auditing of deployments.